元素大小与位置
总览
- 如果元素被隐藏(如:元素或祖先
display: none、不在文档中),几何信息基本是 0 - 几何信息都是
number类型,单位像素(offsetParent不是几何信息)*Width/Height会对值取整(四舍五入),需要小数使用 elem.getBoundingClientRect()*Left/Top会保留小数
- 几何信息都是只读,除了
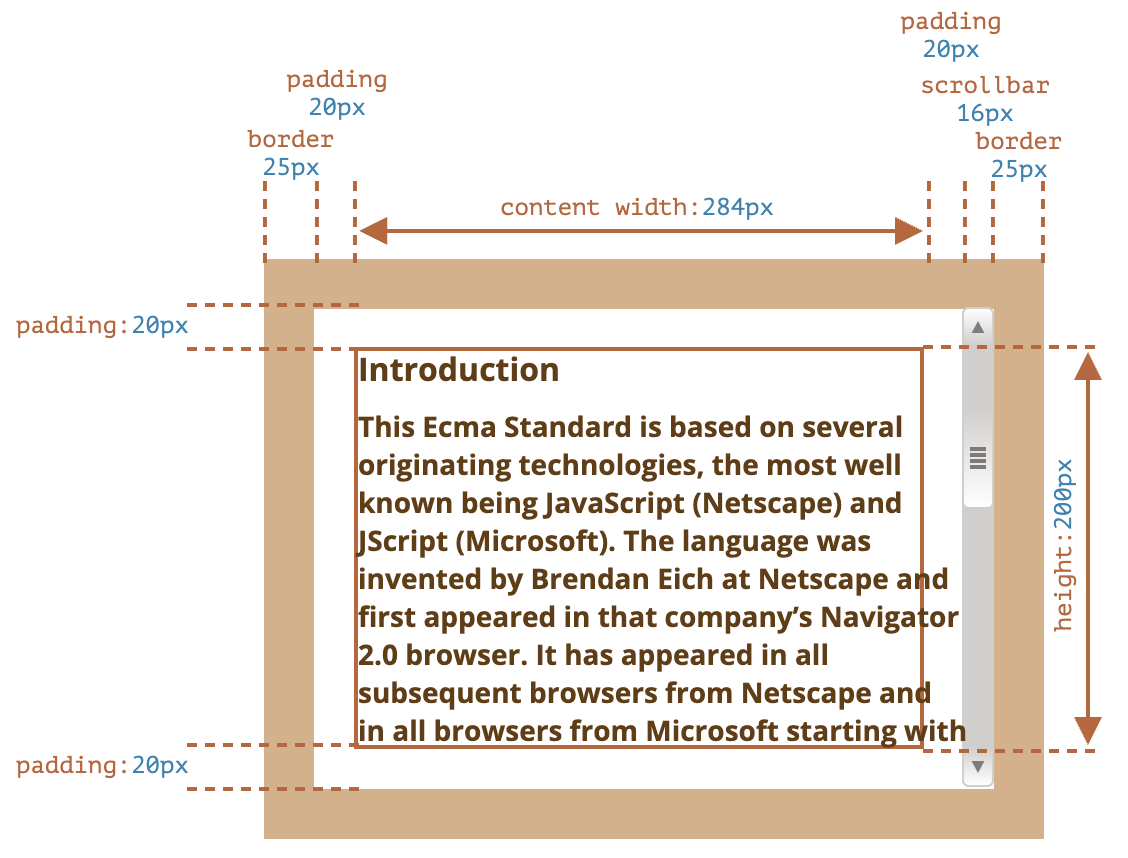
scrollLeft和scrollTop ::before、::after等伪元素属于content- 滚动条在
border和padding之间
offset
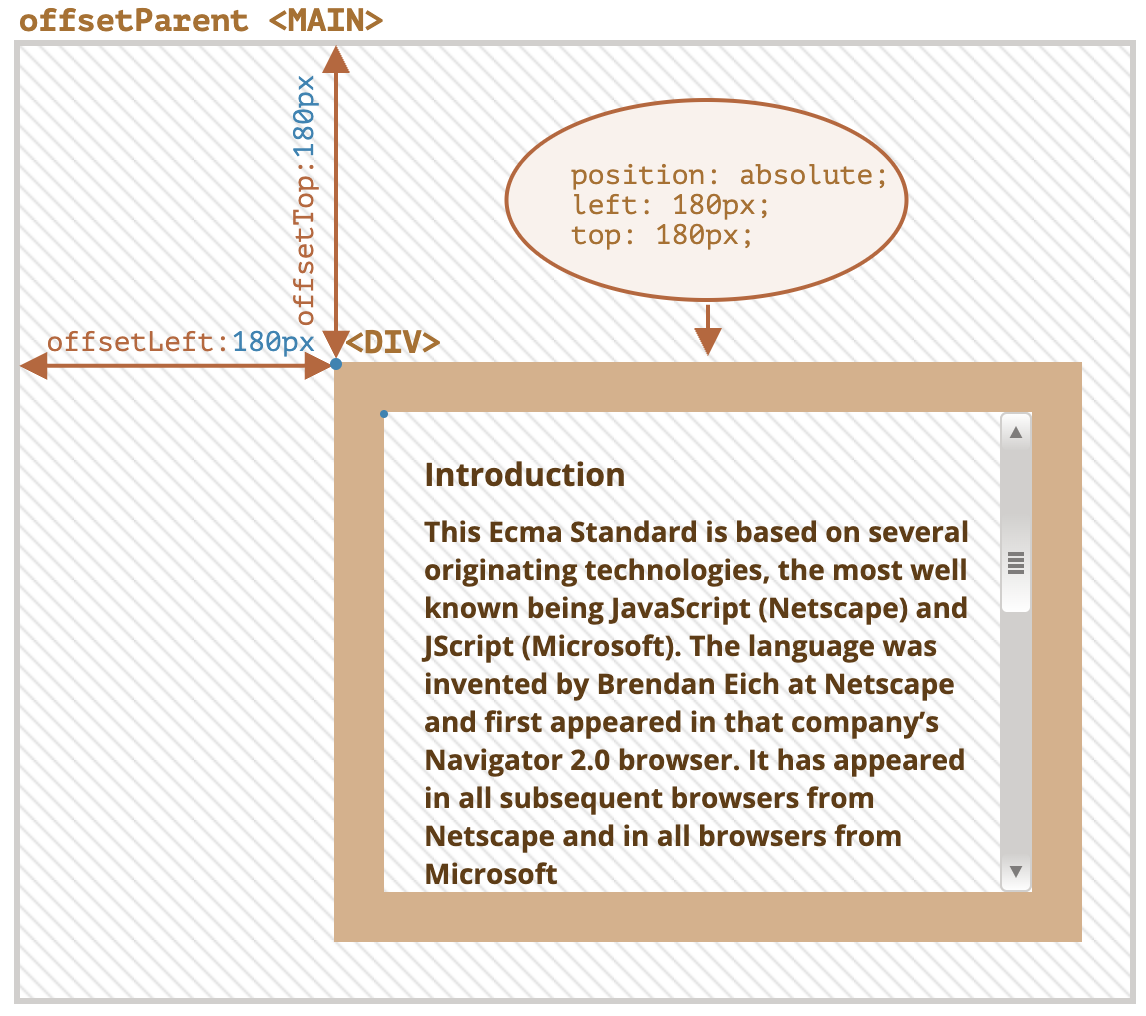
offsetParent:最接近的祖先(ancestor),在浏览器渲染期间,它被用于计算坐标- 只读,返回
Element或null - 最接近的祖先(ancestor):
table、td、th、body元素- CSS 定位元素(
position不为static)
offsetParent值为null的情况:<body>与<html>- 未显示的元素(
display: none或不在文档中) position: fixed的元素
- 只读,返回
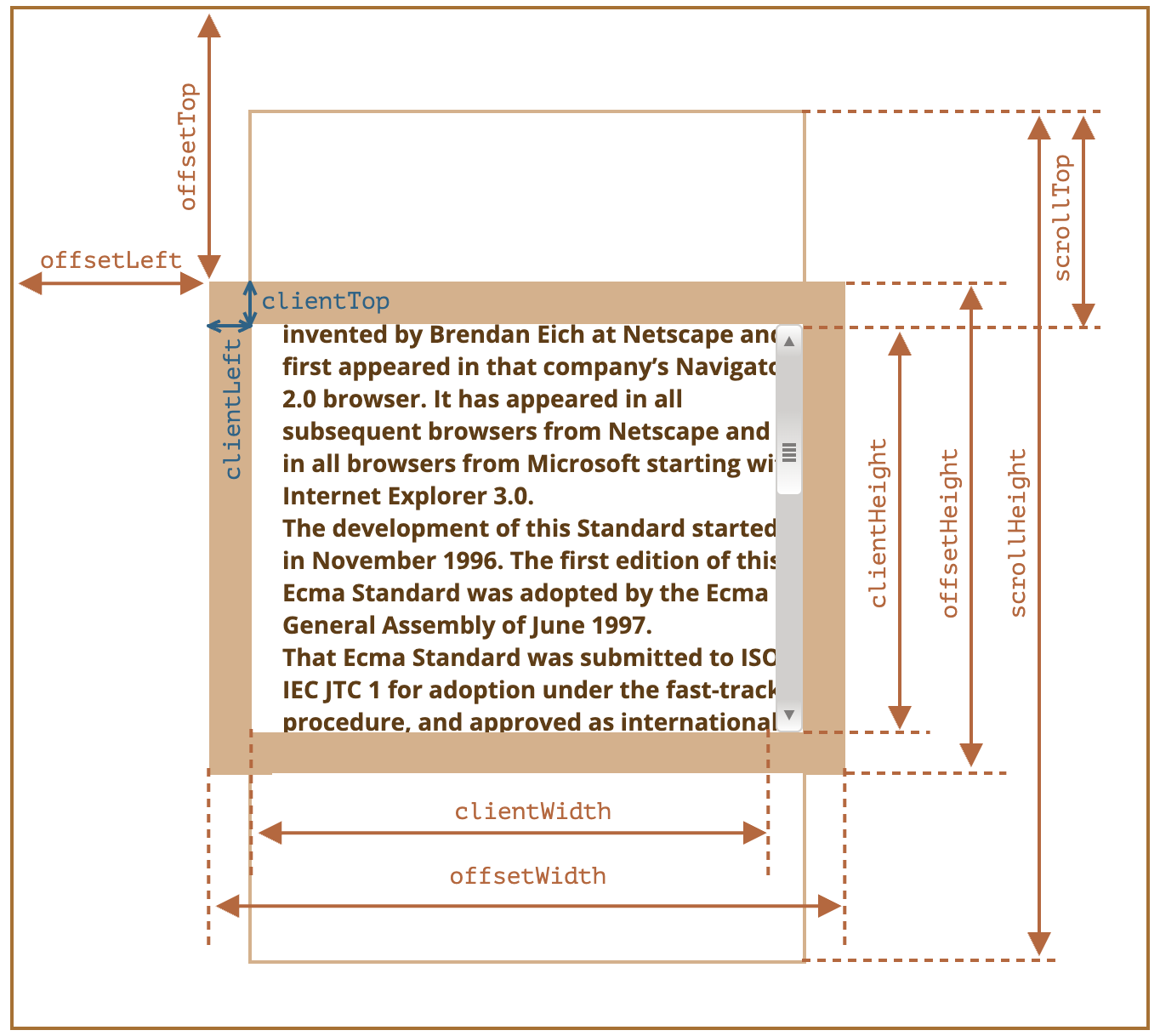
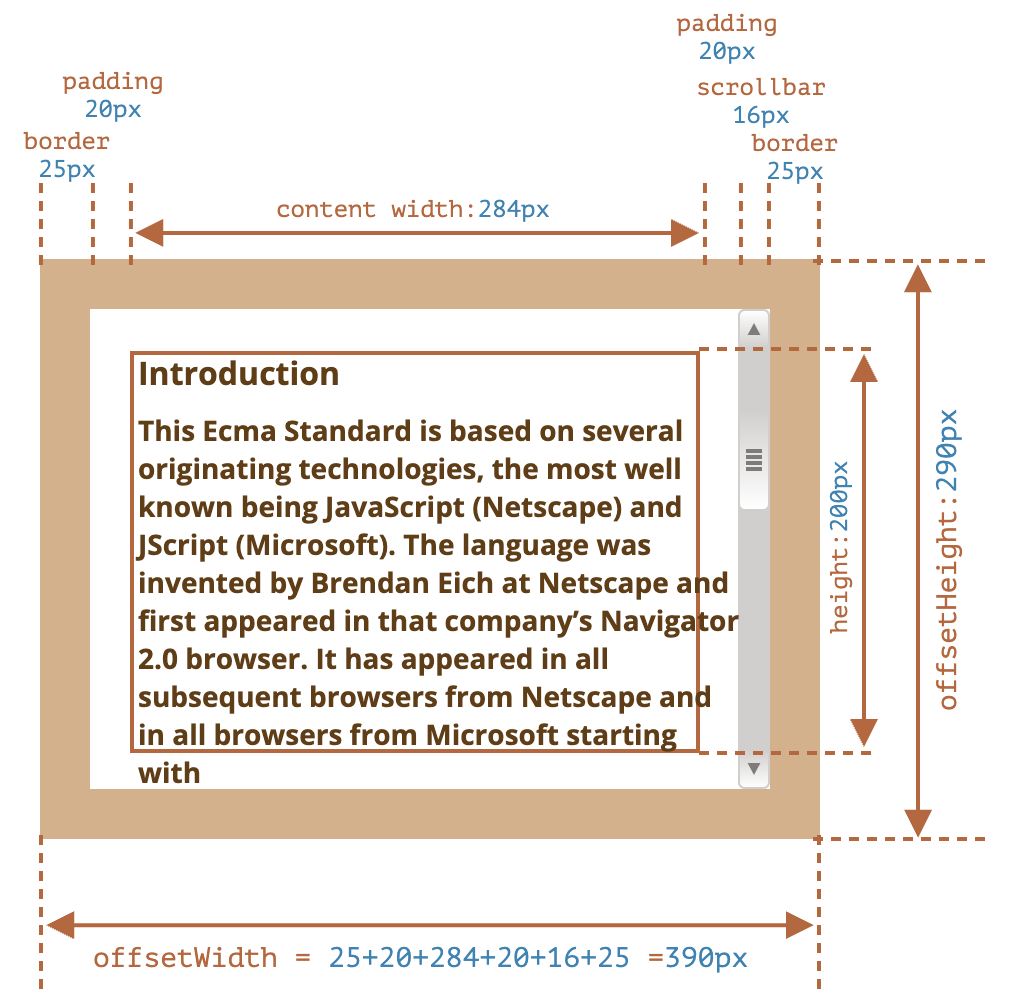
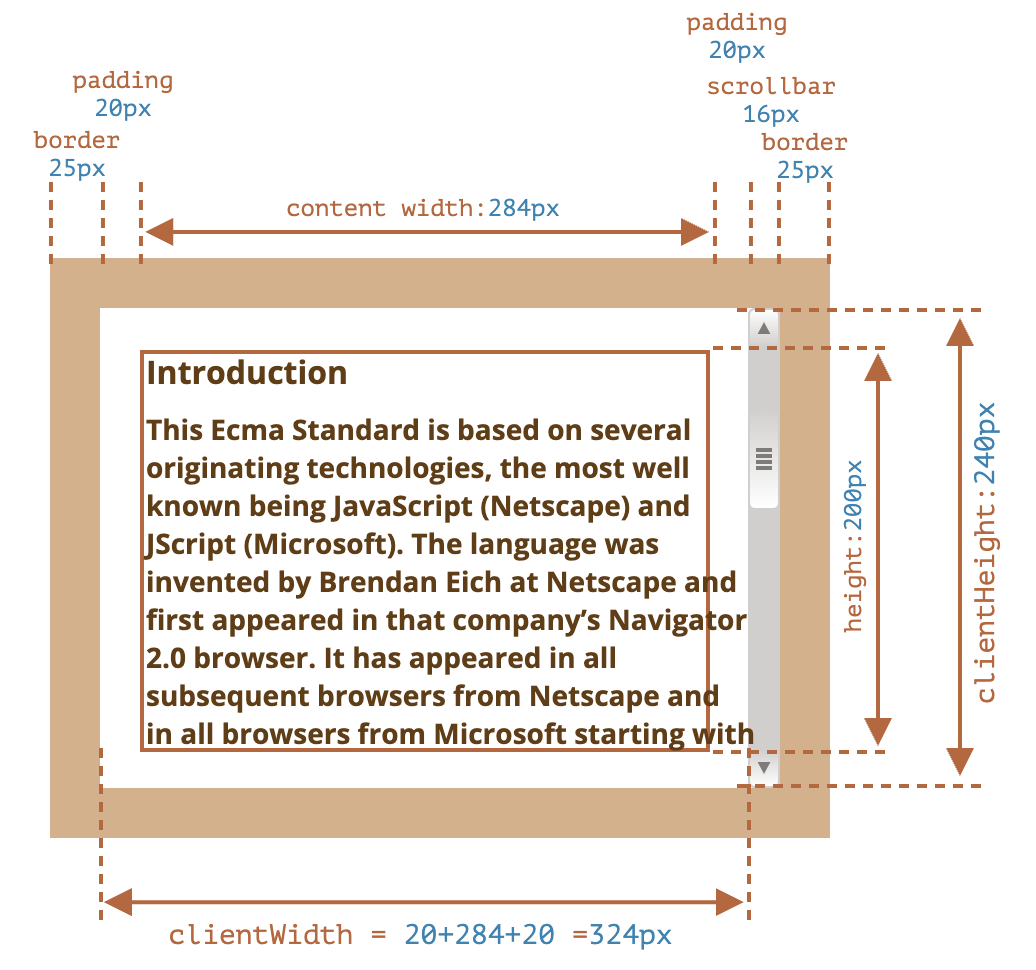
offsetLeft、offsetTop:相对于offsetParent左上角的 X/Y 坐标offsetWidth、offsetHeight:元素的“外部”宽高- 包含
border、padding、content、滚动条 - 对于 body,包括代替元素的 CSS 宽高线性总含量。浮动元素的延伸内容宽高被忽略
- 包含
client
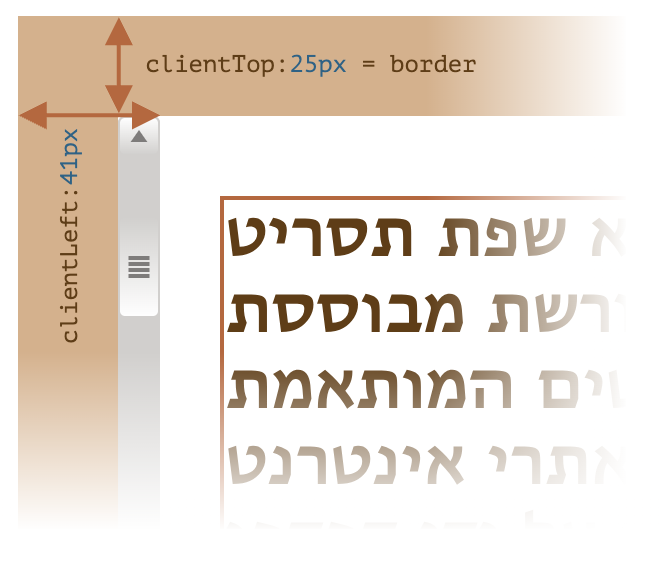
clientLeft、clientTop:元素“内侧”与“外侧”的相对坐标- 包含
border、滚动条
- 包含
clientWidth、clientHeight:元素的“内部”宽高- 包含
padding、content - 不包含滚动条
- 特例:
<html>和怪异模式下的<body>,返回视口宽高(不包含滚动条)
- 包含
scroll
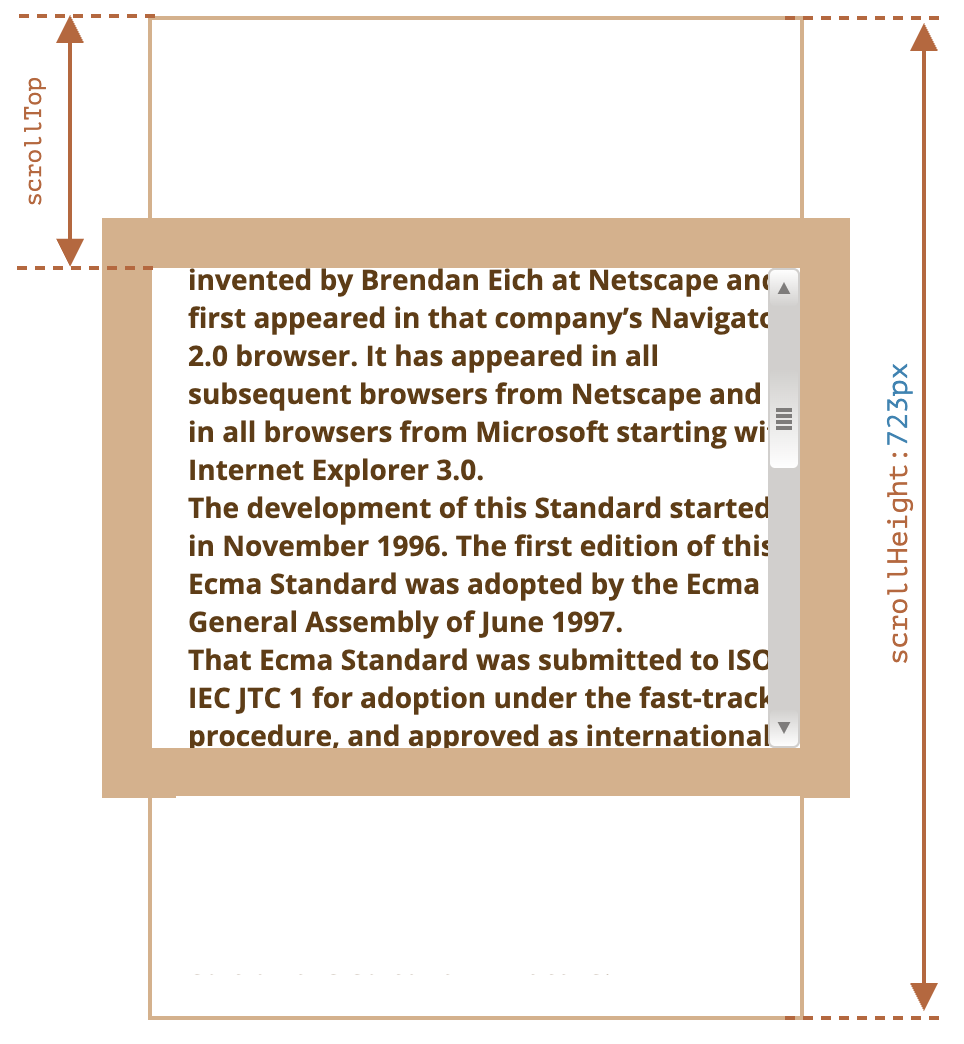
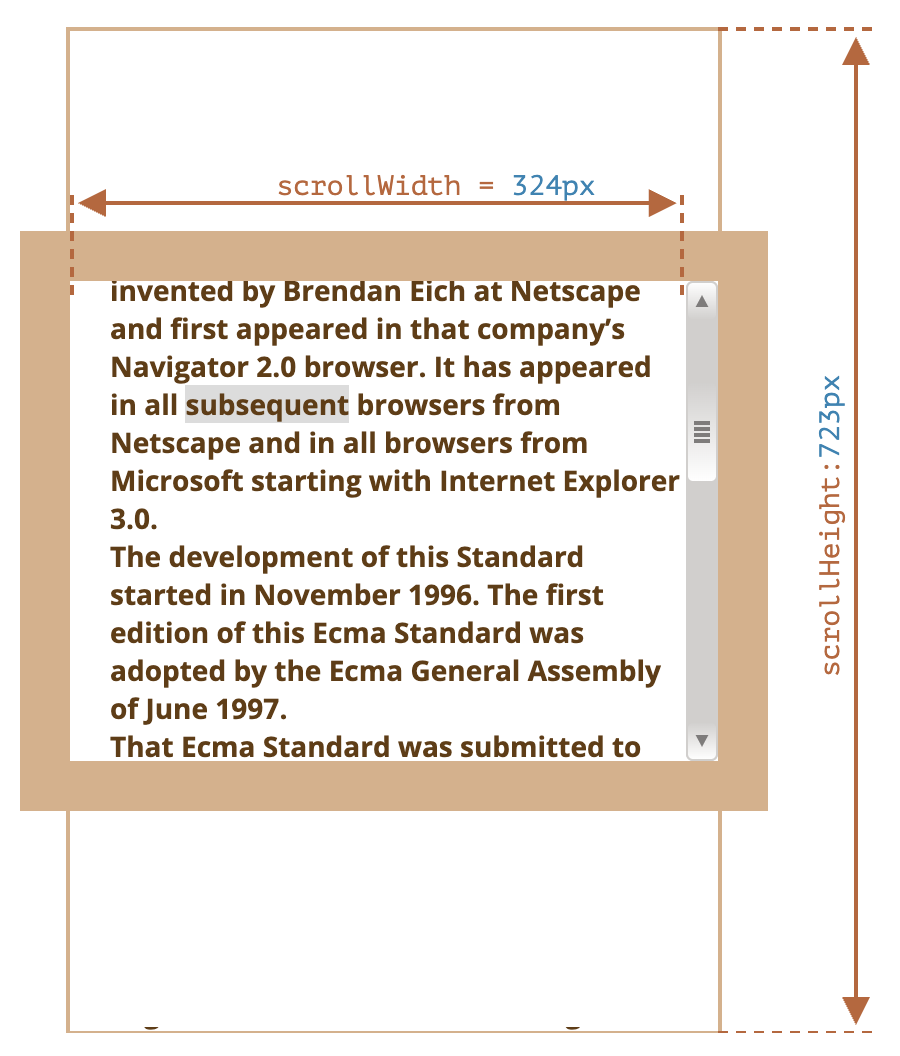
scrollLeft、scrollTop:就像clientLeft、clientTop,但它们还包括滚动出(隐藏)的部分- 可读可写
- 包含
border、滚动条
scrollWidth、scrollHeight:就像clientWidth、clientHeight,但它们还包括滚动出(隐藏)的部分- 包含
padding、content - 不包含滚动条
- 包含
窗口大小与位置
窗口(视口)宽高
使用 document.documentElement.clientWidth/clientHeight
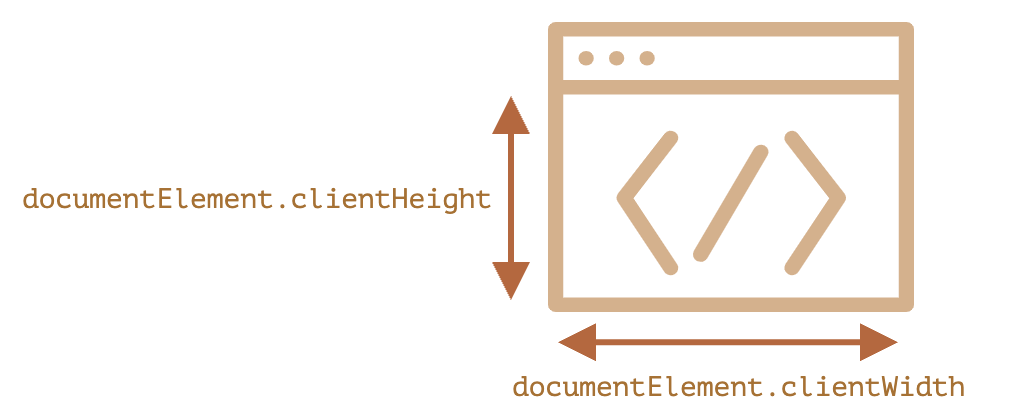
而不是 window.innerWidth/innerHeight,因为其包含滚动条
在大多数情况下,我们需要可用的窗口宽度以绘制或放置某些东西
文档的宽高
从理论上讲,可以使用 document.documentElement.scrollWidth/scrollHeight 来测量文档的完整大小,但由于历史原因,这无法正常工作。
为了可靠地获得完整的文档宽高,应该采用以下这些属性的最大值:
const scrollHeight = Math.max(
document.body.scrollHeight, document.documentElement.scrollHeight,
document.body.offsetHeight, document.documentElement.offsetHeight,
document.body.clientHeight, document.documentElement.clientHeight
)
const scrollWidth = Math.max(
document.body.scrollWidth, document.documentElement.scrollWidth,
document.body.offsetWidth, document.documentElement.offsetWidth,
document.body.clientWidth, document.documentElement.clientWidth
)获得当前滚动
- 使用
document.documentElement.scrollLeft/scrollTop在大多数浏览器中都是正确的 - 在较旧的基于 WebKit 的浏览器应该使用
document.body而不是document.documentElement - 最好使用:
window.pageXOffset/pageYOffset- 只读
- 由于历史原因:
window.pageXOffset是window.scrollX的别名;window.pageYOffset是window.scrollY的别名。
滚动
滚动方法
window:
window.scrollTo():滚动到文档中的某个坐标(绝对位置)scrollTo(x: number, y: number)x:X 轴坐标y:Y 轴坐标
scrollTo({ left: number; top: number; behavior?: string })left:同x-coord,X 轴坐标top:同y-coord,Y 轴坐标behavior:滚动行为,取值如下: ^1"auto":默认值window由浏览器决定elem由 CSSscroll-behavior的计算值决定
"smooth":平滑滚动"instant":瞬间滚动
window.scroll():同window.scrollTo()window.scrollBy():按指定的偏移量滚动文档(相对于当前位置)- 参数同
window.scrollTo()
- 参数同
window.scrollByLines(lines: number):按给定的行数滚动文档lines:要滚动的行数,可以是正整数(向下),也可以是负整数(向上)- 该 API 是非标准的,而且支持程度很差
window.scrollByPages(pages):在当前文档页面按照指定的页数翻页pages:要滚动的页数,可以是正整数(向下),也可以是负整数(向上)- 该 API 是非标准的,而且支持程度很差
// 该方法没有任何意义,且有 BUG:在上一次方法动画没执行完前再次调用,页面就会乱动
// 请使用 window.scrollTo({ left: number; top: number; behavior: "smooth" })
/**
* @description: 平滑滚动文档到指定位置
* @param {number} x 滚动到的 X 轴坐标
* @param {number} y 滚动到的 Y 轴坐标
*/
function smoothScrollTo(x, y) {
// 当前位置
let scrollLeft = document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft
let scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop
function _step() {
// 距离目标距离
const distanceX = x - scrollLeft
const distanceY = y - scrollTop
// 目标位置
scrollLeft = scrollLeft + distanceX / 5
scrollTop = scrollTop + distanceY / 5
if (Math.max(Math.abs(distanceX), Math.abs(distanceY)) < 1) {
window.scrollTo(x, y)
} else {
window.scrollTo(scrollLeft, scrollTop)
requestAnimationFrame(_step)
}
}
_step()
}elem:
elem.scrollTo():同window.scrollTo()elem.scrollBy():同window.scrollBy()elem.scrollIntoView():会滚动元素的父容器,使elem元素出现到可视区域scrollIntoView(alignToTop?: boolean)true:默认值,元素的顶端将和其所在滚动区的可视区域的顶端对齐false:元素的底端将和其所在滚动区的可视区域的底端对齐
scrollIntoView({ inline?: string; block?: string; behavior?: string })inline:定义水平方向的对齐,默认值"nearest",取值如下:"start""center""end""nearest"
block:定义垂直方向的对齐,默认值"start",取值同inlinebehavior:滚动行为,取值 同上
禁止滚动
- 禁止滚动:
document.body.style.overflow = "hidden" - 恢复滚动:
document.body.style.overflow = ""
可以使用相同的技术来冻结其他元素的滚动,而不仅仅是 document.body
这个方法的缺点是会使滚动条消失。如果滚动条占用了一些空间,它原本占用的空间就会空出来,那么内容就会“跳”进去以填充它。
解决方法是对比冻结前后的 clientWidth。如果它增加了(滚动条消失后),就在 document.body 滚动条原来的位置处添加 padding。保持了滚动条冻结前后文档内容宽度相同
坐标
两种坐标系
大多数 JS 方法处理的是以下两种坐标系中的一个:
- 相对于窗口:类似于
position: fixed,从窗口的顶部/左侧边缘计算得出- 将这些坐标表示为
clientX/clientY
- 将这些坐标表示为
- 相对于文档:与文档根(document root)中的
position: absolute类似,从文档的顶部/左侧边缘计算得出- 将这些坐标表示为
pageX/pageY
- 将这些坐标表示为
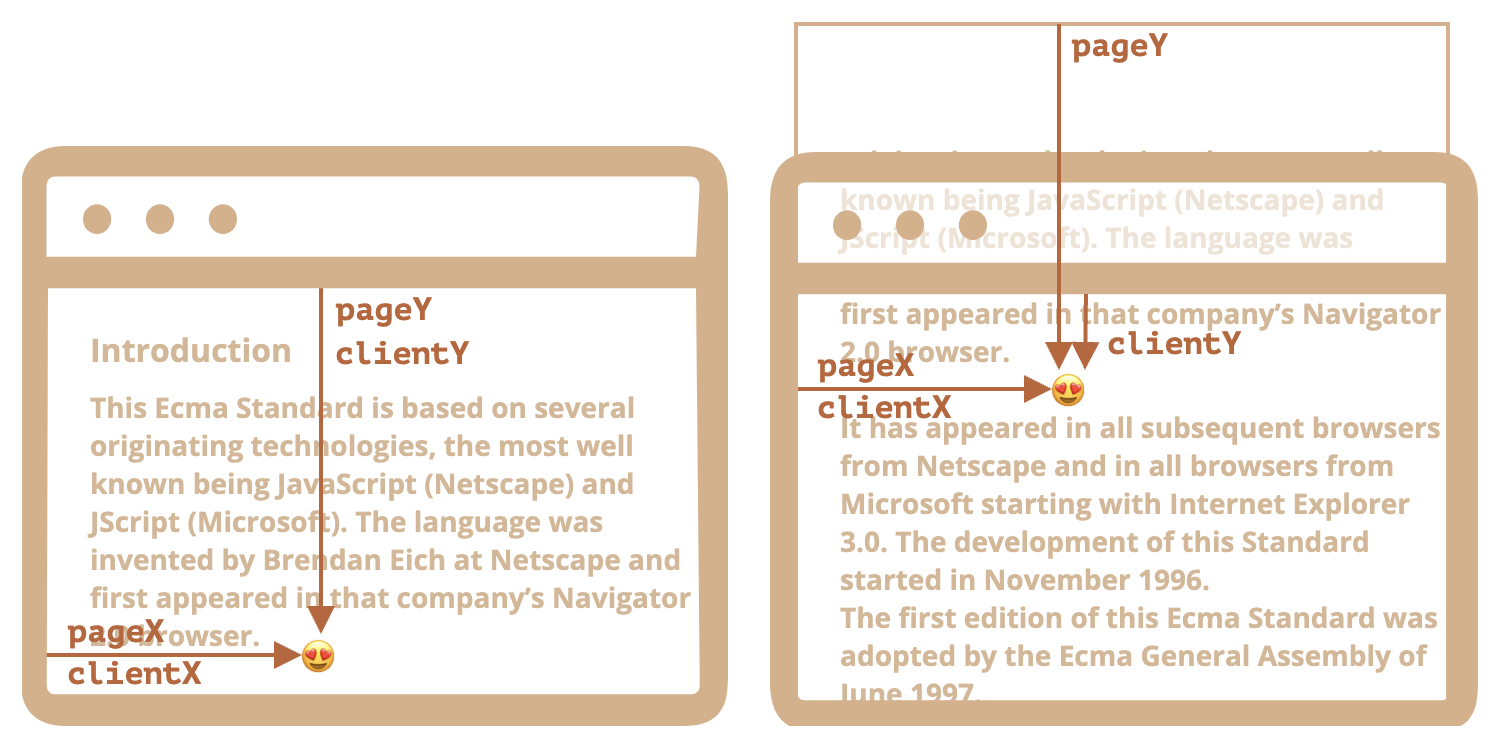
当文档滚动了:
pageY:元素在文档中的相对坐标保持不变,从文档顶部(现在已滚动出去)开始计算clientY:窗口相对坐标发生了变化,因为同一个点越来越靠近窗口顶部
获取元素大小和窗口坐标
elem.getBoundingClientRect() 方法返回一个 DOMRect 对象,提供了元素的最小矩形大小及相对于窗口(视口)的位置。
主要的 DOMRect 属性:
x/y—— 矩形原点相对于窗口的 X/Y 坐标width/height—— 矩形的 width/height,包含border、padding、content、滚动条
此外,还有派生(derived)属性:
top/bottom—— 顶部/底部矩形边缘的 Y 坐标left/right—— 左/右矩形边缘的 X 坐标
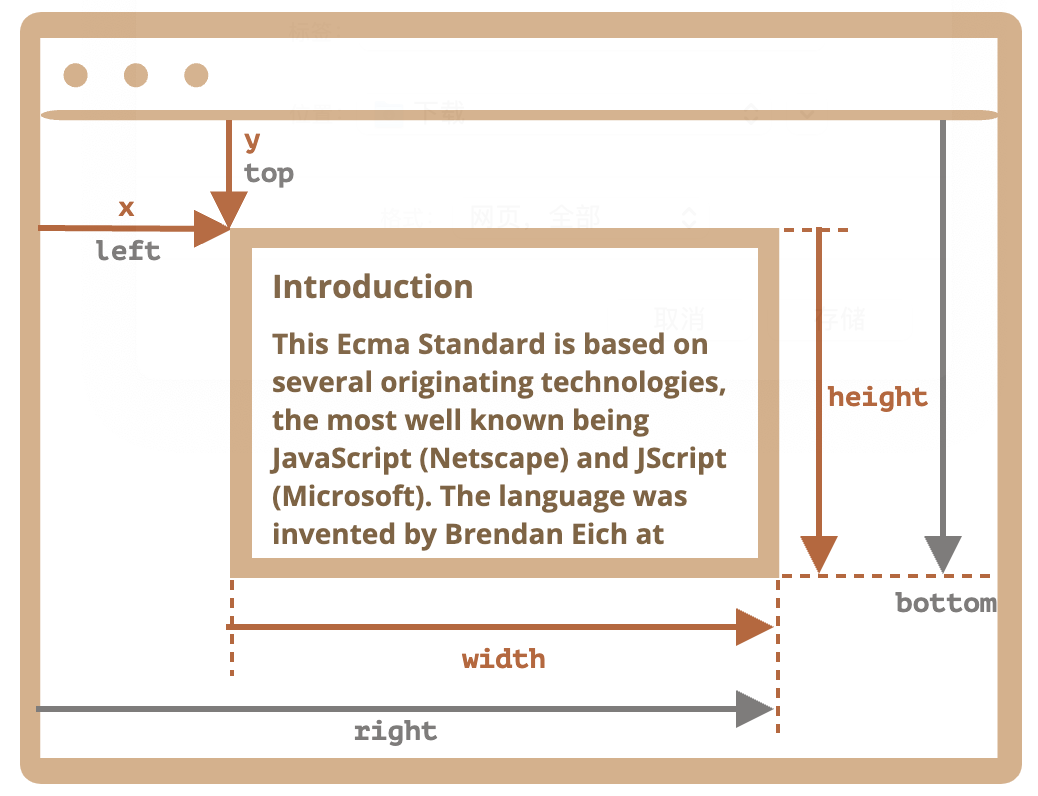
x/y 和 width/height 对矩形进行了完整的描述。可以很容易地从它们计算出派生(derived)属性:
left = xtop = yright = x + widthbottom = y + height
为什么需要派生(derived)属性:
- 为了方便和语义
- 从技术上讲,
width/height可以为负数,从而允许“定向(directed)”矩形- 负的
width/height值表示矩形从其右下角开始,然后向左上方“增长” - 例如代表带有正确标记的开始和结束的鼠标选择
- 但是实际上,
elem.getBoundingClientRect()总是返回正数的width/height
- 负的
注意:
- 值可能是小数
- 坐标可能是负数。例如滚动页面,使
elem位于窗口的上方,则top为负数 - 坐标的
right/bottom与 CSS position 属性不同- CSS position:元素距右/下边缘的距离
getBoundingClientRect:所有坐标都从窗口左上角开始计数
通过窗口坐标获取元素
document.elementFromPoint(x, y) 方法返回在窗口坐标 (x, y) 处嵌套最多/深(the most nested)的元素(z-index 最大的元素)
注意:
- 传入的坐标在窗口(视口)之外,返回
null
获取文档坐标
pageY=clientY+ 文档的垂直滚动出的部分的高度pageX=clientX+ 文档的水平滚动出的部分的宽度
// 获取元素的文档坐标
function getCoords(elem) {
const box = elem.getBoundingClientRect()
return {
top: box.top + window.pageYOffset,
right: box.right + window.pageXOffset,
bottom: box.bottom + window.pageYOffset,
left: box.left + window.pageXOffset
}
}注意
读取几何信息可能导致回流
不要从 CSS 中获取宽高
不要使用像 getComputedStyle 这样的 API 获取元素宽高
原因:
- CSS
width/height取决于另一个属性:box-sizing - 元素真实宽高可能受 CSS 的
min/max-width/height影响 - CSS 的
width/height可能是auto,例如内联(inline)元素 - 出现滚动条时,CSS
width/height取值,不同浏览器的差异较大
常见问题与解决方案
判断元素是否滚动到底
scrollTop 是一个非整数,而 scrollHeight 和 clientHeight 是四舍五入的,因此确定滚动区域是否滚动到底的唯一方法是查看滚动量是否足够接近某个阈值(在本例中为 1):
Math.abs(element.scrollHeight - element.clientHeight - element.scrollTop) < 1判断元素是否能滚动
window.getComputedStyle(element).overflowY === "visible"
window.getComputedStyle(element).overflowY !== "hidden"在某元素附近展示内容
// 在 elem 下显示 html 内容
function createMessageUnder(elem, html) {
let message = document.createElement('div')
// 在这里最好使用 CSS class 来定义样式
message.style.cssText = "position: fixed; color: red"
// 分配坐标
let coords = elem.getBoundingClientRect()
message.style.left = coords.left + "px"
message.style.top = coords.bottom + "px"
message.innerHTML = html
return message
}
// 使用:
let message = createMessageUnder(elem, 'Hello, world!')
document.body.append(message)
setTimeout(() => message.remove(), 5000)上面方法使用的是相对于窗口的坐标(getBoundingClientRect),页面滚动会导致“分离”
要改变这一点,需要使用基于文档(document)的坐标和 position: absolute 样式:
// 在 elem 下显示 html 内容
function createMessageUnder(elem, html) {
let message = document.createElement('div')
message.style.cssText = "position: absolute; color: red" // 相对定位
let coords = getCoords(elem) // 使用相对于文档的坐标
message.style.left = coords.left + "px"
message.style.top = coords.bottom + "px"
message.innerHTML = html
return message
}其中 getCoords 方法 见上